Risk Management Outline
Risk Management in Trading Overview
In the dynamic realm of trading, effective risk management in Trading is paramount for sustained success. While trading presents lucrative profit opportunities, it also carries inherent risks that can result in substantial losses if not managed correctly. This detailed guide will explore the fundamental principles and practical applications of risk management in trading, equipping you to safeguard your investments and minimize potential losses. Whether you are a novice trader or a seasoned professional, grasping and implementing robust risk management strategies is indispensable.
Understanding Risk Management in Trading
Risk management in trading encompasses the identification, assessment, and prioritization of risks, followed by strategic measures to reduce, monitor, and control the likelihood and impact of unfavorable events. It involves recognizing the risks associated with trading and devising approaches to mitigate these risks to ensure sustained profitability.
Detailed Definitions:
1. Risk Identification:
Risk identification is the process of determining what risks exist that could potentially affect the trading strategy. These risks can be market risks, liquidity risks, and operational risks.
- Market Risk: Exposure to losses due to market price fluctuations.
- Liquidity Risk: Risk of being unable to swiftly buy or sell assets without significant price alterations.
- Operational Risk: Risks stemming from operational glitches like system failures or human errors.
2. Risk Assessment:
Once risks are identified, they must be evaluated in terms of their potential impact and likelihood.
- Impact: Estimating the financial loss potential of a risk.
- Likelihood: Assessing the probability of a risk occurring.
3. Risk Prioritization:
Not all risks carry the same weight. Prioritizing risks involves managing the most impactful and likely risks first.
4. Risk Mitigation:
Developing strategies to minimize identified risks, such as diversifying the portfolio, using stop-loss orders, and establishing risk-reward ratios.
5. Risk Monitoring:
Continuously reviewing and adjusting risk management strategies to ensure their effectiveness as market conditions and personal situations evolve.
Significance of Risk Management
Effective risk management is essential for successful trading, offering several crucial benefits that can significantly impact a trader’s long-term success. Here we explore these benefits in detail, supported by statistical data and expert opinions.
Preservation of Capital:
The primary objective of risk management is to safeguard your trading capital. Without adequate capital, you cannot participate in trading. Research shows that traders who implement risk management strategies are more likely to preserve their capital during market downturns. According to a study by the CFA Institute, traders who use stop-loss orders reduce their risk of significant losses by up to 50%.
Sustainability:
Effective risk management enables traders to sustain their trading endeavors over the long haul, regardless of market conditions. A report by JP Morgan Asset Management found that portfolios with diversified assets are less volatile and more likely to generate consistent returns over time. This diversification mitigates the impact of any single asset’s poor performance.
Confidence Boost:
Managing risks allows traders to trade with increased confidence, knowing that potential losses are controlled. A survey by the National Futures Association revealed that 75% of successful traders attribute their confidence to robust risk management practices. This confidence is crucial for making rational decisions rather than emotional ones.
Consistency:
Risk management aids in achieving consistent returns by minimizing substantial losses. Data from the Financial Analysts Journal indicates that traders who maintain a disciplined risk management approach achieve more stable returns compared to those who do not. Consistency in returns builds a reliable track record, which is essential for long-term success.
Statistical Data on Risk Management Impact:
•A study by the Journal of Portfolio Management found that portfolios with a well-implemented risk management strategy outperform those without such strategies by an average of 2% annually.
•According to Morningstar, funds that actively manage risk through diversification and hedging have a lower standard deviation, indicating reduced volatility and risk.
Quotes from Industry Experts:
1. Warren Buffett: “Risk comes from not knowing what you’re doing. Effective risk management is essential for understanding and mitigating those risks.”
2. Ray Dalio: “He who lives by the crystal ball will eat shattered glass. The key to success is to manage risk effectively.”
3. Paul Tudor Jones: “The most important rule of trading is to play great defense, not great offense. This means managing risk rigorously.”
By understanding and appreciating the significance of risk management, traders can build a solid foundation for long-term success in the markets.
Transitioning into the next section, we will delve into the fundamental principles of risk management, detailing the steps involved in identifying, assessing, prioritizing, and mitigating risks.
Next, we will explore the fundamental principles of risk management. This section will outline the key steps involved in the risk management process, including risk identification, assessment, prioritization, mitigation, and monitoring.
Fundamental Principles of Risk Management
Risk management in trading involves a systematic approach to identifying, assessing, prioritizing, mitigating, and monitoring risks. By understanding and applying these fundamental principles, traders can better protect their investments and improve their chances of long-term success.
1. Risk Identification
Risk identification is the first step in the risk management process. It involves recognizing potential risks that could affect trading performance. These risks can be broadly categorized into market risks, liquidity risks, and operational risks.
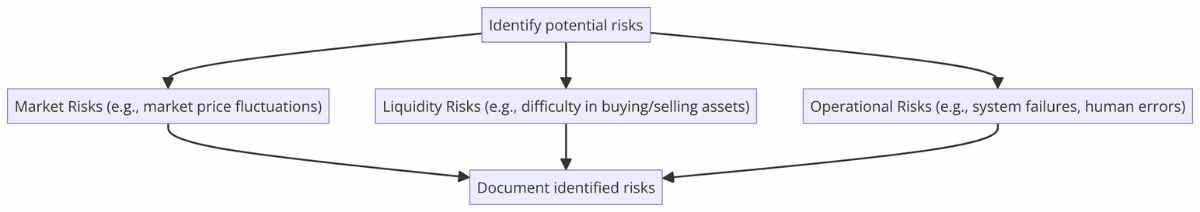
- Market Risk: Exposure to losses due to market price fluctuations. For instance, a trader holding a long position in a volatile stock faces market risk as the stock price can move significantly in either direction.
- Liquidity Risk: Risk of being unable to swiftly buy or sell assets without significant price alterations. For example, a trader trying to sell a large position in a thinly traded stock may face liquidity risk.
- Operational Risk: Risks stemming from operational glitches like system failures or human errors. An example could be a trader making an incorrect trade entry due to a typo.
2. Risk Assessment
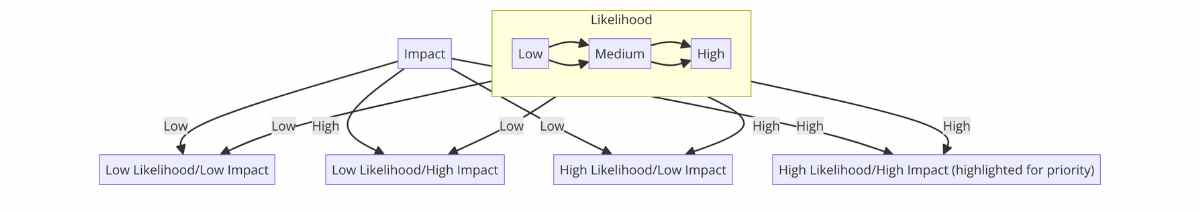
After identifying risks, the next step is to assess their potential impact and likelihood. This involves estimating the financial loss potential (impact) and the probability of a risk occurring (likelihood).
- Impact: Estimating the financial loss potential of a market downturn on a portfolio.
- Likelihood: Assessing the probability of a system failure during high trading volumes.
3. Risk Prioritization
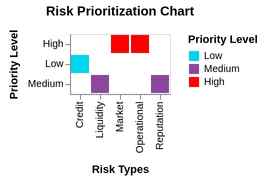
Not all risks carry the same weight. Risk prioritization involves managing the most impactful and likely risks first. This step ensures that resources are focused on the areas that could cause the most significant damage.
- Prioritizing the mitigation of high-probability market risks over lower-probability operational risks.
- Addressing risks with the highest potential financial impact first.
4. Risk Mitigation
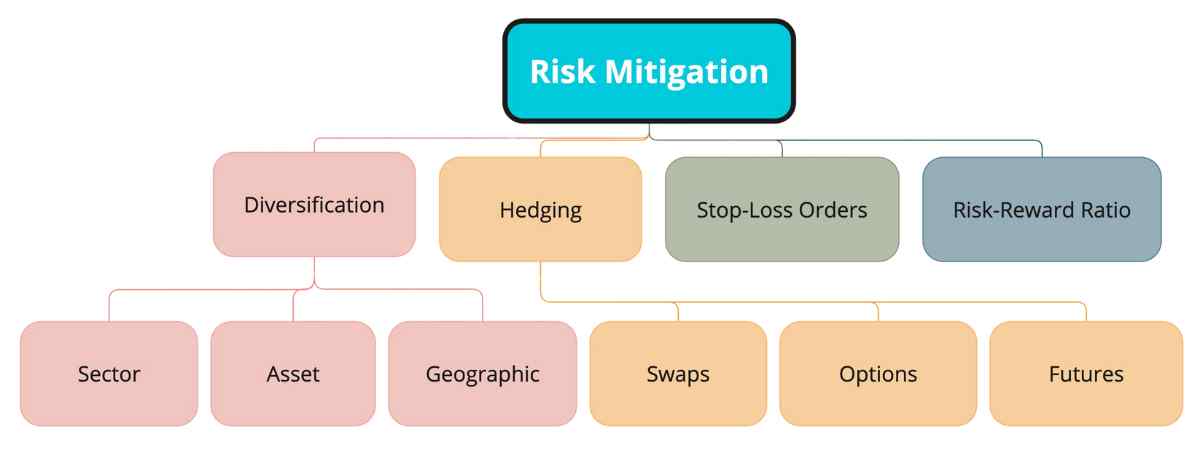
Risk mitigation involves developing strategies to minimize identified risks. This can be achieved through various methods such as diversification, stop-loss orders, and establishing risk-reward ratios.
- Diversification: Spreading investments across various assets to reduce exposure to individual asset risk.
- Stop-Loss Orders: Setting a predetermined price at which a trade will be exited to prevent further losses.
- Risk-Reward Ratio: Establishing a ratio to evaluate trade profitability relative to risk.
5. Risk Monitoring
The final step is risk monitoring, which involves continuously reviewing and adjusting risk management strategies to ensure their effectiveness. As market conditions and personal circumstances change, risk management strategies must be adaptable.
- Regularly reviewing portfolio performance and adjusting strategies based on current market conditions.
- Updating stop-loss levels and diversification strategies as needed.
By understanding and applying these fundamental principles of risk management, traders can develop a robust framework to protect their investments and enhance their trading performance.
Transitioning into the next section, we will explore various effective risk management strategies that traders can implement to further safeguard their portfolios.
Next, we will delve into effective risk management strategies. This section will provide detailed explanations and examples of strategies such as diversification, position sizing, stop-loss orders, risk-reward ratios, hedging, and leverage management.
Effective Risk Management Strategies

1. Diversification
Case Study:
Step-by-Step Guide:
2. Position Sizing
Example:
Position Size = (Account Risk × Account Balance) / Stop Loss
3. Stop-Loss Orders
Example:
Step-by-Step Guide:
4. Risk-Reward Ratio
Example:
Step-by-Step Guide:
Risk-Reward Ratio = Potential Loss / Potential Gain
5. Hedging
6. Leverage Management
Example:
Step-by-Step Guide:
Advanced Risk Management Techniques

Value at Risk (VaR) is a statistical method to measure the risk of loss on a specific financial asset or portfolio. It estimates the maximum potential loss over a specified period within a given confidence level.
1. Value at Risk (VaR)
Value at Risk (VaR) is a statistical method to measure the risk of loss on a specific financial asset or portfolio. It estimates the maximum potential loss over a specified period within a given confidence level.
Calculation:
Variance-Covariance Method:
- Determine the Portfolio Mean Return (µ ) and Standard Deviation ( ):
- Calculate the mean return of the portfolio.
- Calculate the standard deviation of the portfolio returns.
- Choose a Confidence Level:
- Common confidence levels are 95% and 99%.
- Calculate VaR:
VaR = µ – Z · σ
where Z is the Z-score corresponding to the chosen confidence level (e.g., 1.65 for 95%, 2.33 for 99%).
Example:
VaR = 0.1% – 1.65 x 2% = 0.1% – 3.3% = -3.2%
Template:
| Portfolio Mean Return (μ) | Portfolio Standard Deviation (σ) | Confidence Level | Z-score | VaR |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0.1% | 2% | 95% | 1.65 | -3.2% |
2. Stress Testing
Stress testing involves simulating extreme market conditions to assess their impact on your portfolio. It helps traders understand how their portfolios would perform under adverse scenarios.
Steps to Conduct Stress Testing:
1. Identify Stress Scenarios:
- Use historical events (e.g., 2008 financial crisis) or hypothetical situations (e.g., sudden interest rate hike).
2. Simulate the Impact:
- Apply the stress scenario to your portfolio to see how it affects asset prices and portfolio value.
3. Analyze Results:
- Evaluate the potential losses and identify vulnerabilities in your portfolio.
Example:
A portfolio manager wants to stress test their portfolio against a 20% market drop similar to the 2008 financial crisis.
- Calculate the impact of a 20% drop on each asset.
- Sum the losses to determine the overall portfolio impact.
| Asset | Current Value | Stress Scenario (20% Drop) | New Value | Loss |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stock A | $10,000 | -20% | $8,000 | $2,000 |
| Bond B | $15,000 | -20% | $12,000 | $3,000 |
| Total | $25,000 | $20,000 | $5,000 |
3. Scenario Analysis
Scenario analysis entails analyzing potential future events by considering alternative outcomes (scenarios). It helps traders evaluate how different situations might affect their portfolios.
Steps to Conduct Scenario Analysis:
1. Define Scenarios:
- Identify different market scenarios (e.g., bullish, bearish, stagnant).
2. Estimate Impact:
- Assess how each scenario would affect your portfolio.
3. Assign Probabilities:
- Assign probabilities to each scenario based on their likelihood.
4. Analyze Results:
- Calculate the expected portfolio value and potential risks for each scenario.
Example:
A trader considers three scenarios for the next year: Bullish (50% probability), Bearish (30% probability), and Stagnant (20% probability).
| Scenario | Probability | Expected Return | Impact on Portfolio |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bullish | 50% | 20% | +$5,000 |
| Bearish | 30% | -10% | -$3,000 |
| Stagnant | 20% | 0% | $0 |
| Total Expected Return | $2,000 |
Practical Example:
A trader wants to evaluate the impact of different economic conditions on their portfolio. They define three scenarios and estimate the portfolio returns for each.
| Technique | Calculation | Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| VaR | 0.1% – 1.65 x 2% | -3.2% | 5% chance of losing more than 3.2% in a day |
| Stress Test | 20% market drop | $80,000 | Portfolio value drops to $80,000 |
| Scenario Analysis | Bullish: 50%, Bearish: 30%, Stagnant: 20% | $107,000 | Expected portfolio value is $107,000 |
Example of Combining Techniques:
- Value at Risk (VaR):
- Calculate the VaR to understand the potential maximum loss under normal market conditions.
- Stress Testing:
- Apply stress testing to see how the portfolio performs under extreme market conditions, such as a sudden market crash or geopolitical event.
- Scenario Analysis:
- Conduct scenario analysis to evaluate the impact of various future market scenarios, such as a bullish market, bearish market, and stagnant market.
Comprehensive Example:
- Initial Value: $100,000
- Assets: Stocks, Bonds, and Commodities
Step-by-Step Process:
- Mean Daily Return: 0.1%
- Daily Standard Deviation: 2%
- Confidence Level: 95%
- VaR Calculation:
VaR = 0.1% – 1.65 x 2% = -3.2%
- Scenario: 20% Market Drop
- Impact on Portfolio:
- Stocks: $50,000 \times 0.8 = $40,000
- Bonds: $30,000 \times 0.8 = $24,000
- Commodities: $20,000 \times 0.8 = $16,000
- Total Loss: $100,000 – $80,000 = $20,000
- Interpretation: The portfolio value drops to $80,000 under extreme market conditions.
- Define Scenarios:
- Bullish: 50% probability, 20% return
- Bearish: 30% probability, -10% return
- Stagnant: 20% probability, 0% return
- Expected Portfolio Value:
- Bullish: $100,000 \times 1.20 = $120,000
- Bearish: $100,000 \times 0.90 = $90,000
- Stagnant: $100,000 \times 1.00 = $100,000
(0.50 \times $120,000) + (0.30 \times $90,000) + (0.20 \times $100,000) = $60,000 + $27,000 + $20,000 = $107,000
| Technique | Calculation | Result | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| VaR | 0.1% – 1.65 x 2% | -3.2% | 5% chance of losing more than 3.2% in a day |
| Stress Test | 20% market drop | $80,000 | Portfolio value drops to $80,000 |
| Scenario Analysis | Bullish: 50%, Bearish: 30%, Stagnant: 20% | $107,000 | Expected portfolio value is $107,000 |
By combining VaR, stress testing, and scenario analysis, traders can develop a comprehensive understanding of potential risks and take proactive steps to mitigate them. These advanced techniques provide valuable insights into the impact of various market conditions on a portfolio, enabling traders to make more informed decisions and enhance their risk management strategies.
Transitioning into the next section, we will explore the psychological aspects of risk management, discussing the importance of emotional discipline, patience, consistency, and continuous improvement in trading.
Next, we will delve into the psychological aspects of risk management. This section will provide insights into the importance of emotional discipline, patience, consistency, and continuous improvement, supported by practical tips and real-world examples.
 Psychological Aspects of Risk Management
Psychological Aspects of Risk Management
Effective risk management extends beyond strategies and tools to include emotional management and discipline. A trader’s mindset plays a critical role in their success. In this section, we will discuss the importance of emotional discipline, consistency, and continuous improvement, supported by practical tips, techniques, and insights from successful traders.
1. Emotional Discipline
Maintaining emotional discipline is crucial in trading. Emotional trading often leads to poor decision-making and significant losses.
Tips and Techniques:
- Set Clear Goals: Define your trading goals and stick to them. Having clear objectives helps maintain focus and avoid impulsive decisions.
- Develop a Trading Plan: A well-structured trading plan includes entry and exit points, risk management strategies, and trading rules. Following a plan reduces emotional interference.
- Use Stop-Loss Orders: Stop-loss orders help manage risk and take emotions out of the equation by automatically exiting trades at predetermined levels.
- Keep a Trading Journal: Documenting your trades and emotions can help identify patterns and improve future decision-making.
- Take Breaks: Regular breaks can help clear your mind and prevent emotional burnout.
Quotes from Successful Traders:
“The most important rule of trading is to play great defense, not great offense. This means managing risk rigorously and not letting emotions dictate your trades.”
Paul Tudor Jones Tweet
“He who lives by the crystal ball will eat shattered glass. The key to success is to manage risk effectively and stay calm under pressure.”
Ray Dalio Tweet
2. Patience and Consistency
Patience and consistency are vital for long-term trading success. Quality trading opportunities do not present themselves every day, and maintaining a disciplined approach is essential.
Tips and Techniques:
- Wait for the Right Setup: Avoid chasing trades. Be patient and wait for setups that meet your criteria.
- Stick to Your Plan: Consistently follow your trading plan and strategies. Deviating from your plan can lead to inconsistency and increased risk.
- Focus on Process, Not Outcomes: Concentrate on executing your strategy correctly rather than obsessing over the results of individual trades.
- Review and Reflect: Regularly review your trading performance and reflect on your adherence to your plan.
Quotes from Successful Traders:
“The stock market is a device for transferring money from the impatient to the patient.”
Warren Buffett Tweet
“After spending many years in Wall Street and after making and losing millions of dollars, I want to tell you this: It never was my thinking that made the big money for me. It always was my sitting.”
Jesse Livermore Tweet
3. Learning from Mistakes
Continuous improvement is essential in trading. Analyzing past trades and learning from mistakes can help traders refine their strategies and avoid repeating errors.
Tips and Techniques:
- Analyze Losses: Review losing trades to understand what went wrong. Look for patterns or mistakes that can be corrected.
- Seek Feedback: Engage with trading communities or mentors to get feedback on your strategies and performance.
- Adapt and Evolve: Markets change, and so should your strategies. Be open to adapting your approach based on new information and experiences.
- Invest in Education: Continuously seek knowledge through books, courses, and seminars to stay updated with market trends and trading techniques.
Quotes from Successful Traders:
“It’s not whether you’re right or wrong that’s important, but how much money you make when you’re right and how much you lose when you’re wrong.”
George Soros Tweet
“Novice traders trade 5 to 10 times too big. They are taking 5 to 10 percent risks on a trade when they should be risking 1 to 2 percent.”
Bruce Kovner Tweet
By incorporating these psychological aspects into your trading routine, you can enhance your ability to manage risk effectively and achieve consistent success. Emotional discipline, patience, and continuous learning are key components of a successful trading mindset.
Transitioning into the next section, we will explore the tools and resources available for risk management, including trading platforms, software, and educational materials.
Next, we will delve into the tools and resources for risk management. This section will cover various trading platforms, risk management software, and educational resources that can aid traders in implementing effective risk management strategies.
 8. Tools and Resources for Risk Management
8. Tools and Resources for Risk Management
Effective risk management in trading requires access to the right tools and resources. In this section, we will review and compare various trading platforms, risk management software, and educational resources that can help traders implement robust risk management strategies.
1. Trading Platforms
Trading platforms are essential for executing trades and managing risk. Here are detailed reviews of some popular trading platforms:
- MetaTrader 4/5 (MT4/MT5):
- Overview: MetaTrader is one of the most widely used trading platforms, known for its user-friendly interface and robust functionality.
- Key Features: Advanced charting tools, automated trading through Expert Advisors (EAs), backtesting capabilities, and a wide range of technical indicators.
- Pros: Highly customizable, supports automated trading, and offers a large community for support and resources.
- Cons: Limited built-in risk management tools; users may need to integrate additional plugins.
- Additional Resources: MetaTrader 4 and MetaTrader 5
- Thinkorswim:
- Overview: Thinkorswim, offered by TD Ameritrade, is a powerful trading platform known for its advanced analytics and research tools.
- Key Features: Real-time data, customizable charts, paper trading, and extensive educational resources.
- Pros: Comprehensive risk management features, strong customer support, and educational content.
- Cons: Can be overwhelming for beginners due to its extensive features.
- Additional Resources: Thinkorswim
- Interactive Brokers (IBKR) TWS:
- Overview: Trader Workstation (TWS) by Interactive Brokers is designed for professional traders and offers a wide range of trading tools.
- Key Features: Advanced order types, risk management tools, portfolio analysis, and real-time monitoring.
- Pros: Extensive range of features, low trading costs, and strong risk management capabilities.
- Cons: Steeper learning curve for new traders.
- Additional Resources: Interactive Brokers TWS
2. Risk Management Software
Risk management software helps traders analyze and manage their portfolios effectively. Here are detailed reviews of some popular risk management tools:
- Riskalyze:
- Overview: Riskalyze is a risk assessment platform that helps traders understand their risk tolerance and align their portfolios accordingly.
- Key Features: Risk assessment, portfolio risk analysis, stress testing, and client risk profiles.
- Pros: User-friendly interface, effective risk assessment, and detailed reports.
- Cons: Primarily designed for financial advisors, may be less suitable for individual traders.
- Additional Resources: Riskalyze
- TradeStops:
- Overview: TradeStops offers advanced risk management and portfolio management tools, focusing on position sizing and stop-loss strategies.
- Key Features: Position sizing calculators, stop-loss management, portfolio tracking, and alerts.
- Pros: Easy to use, helps in optimizing risk and return, and integrates well with brokerage accounts.
- Cons: Subscription-based service can be expensive for some users.
- Additional Resources: TradeStops
- Portfolio123:
- Overview: Portfolio123 is a platform that provides tools for portfolio construction, backtesting, and risk management.
- Key Features: Customizable screening tools, backtesting, portfolio simulation, and risk analysis.
- Pros: Comprehensive tools for building and managing portfolios, robust backtesting capabilities.
- Cons: Can be complex for beginners, requires some learning to use effectively.
- Additional Resources: Portfolio123
3. Educational Resources
Continuous learning is crucial for effective risk management. Here are some valuable educational resources:
Books:
- “The Essentials of Risk Management” by Michel Crouhy, Dan Galai, and Robert Mark: This book provides a comprehensive overview of risk management concepts and practices.
- “Trading for a Living” by Dr. Alexander Elder: A classic book that covers trading psychology, risk management, and technical analysis.
Online Courses:
- Coursera: Offers a variety of courses on risk management, trading, and financial markets. Coursera Risk Management Courses
- Udemy: Provides courses on trading strategies, risk management, and financial analysis. Udemy Trading Courses
Webinars and Online Communities:
- Investing.com: Offers free webinars on various trading topics, including risk management. Investing.com Webinars
- TradingView: An online community where traders share ideas, strategies, and analysis. TradingView
- Elite Trader: A forum for traders to discuss strategies, tools, and risk management techniques. Elite Trader
By leveraging these tools and resources, traders can enhance their risk management practices and improve their overall trading performance. Whether you are looking for advanced trading platforms, specialized risk management software, or educational materials, these resources provide valuable support for effective risk management.
Transitioning into the next section, we will explore real-world applications of risk management through detailed case studies, highlighting lessons learned from both successes and failures in the trading world.
Next, we will delve into case studies that demonstrate real-world applications of risk management. This section will highlight lessons learned from both successful and failed examples in the trading world.
Case Studies: Real-World Applications of Risk Management
Learning from real-world examples of risk management can provide valuable insights into effective strategies and common pitfalls. This section examines several case studies from different market conditions and asset classes, analyzing what went right and what went wrong.
Case Study 1: The 2008 Financial Crisis

Overview:
The 2008 financial crisis was a severe worldwide economic crisis that occurred in the late 2000s. It was the most serious financial crisis since the Great Depression (1929). The crisis began with the collapse of the housing bubble in the United States, which led to a global banking crisis.
What Went Wrong:
- Leverage: Financial institutions had high leverage ratios, which amplified their losses when housing prices fell.
- Risk Management Failures: Many institutions underestimated the risk of mortgage-backed securities and failed to manage these risks effectively.
- Lack of Diversification: Heavy investments in housing-related assets led to significant losses when the housing market collapsed.
Lessons Learned:
•Importance of Leverage Management: Properly managing leverage can prevent catastrophic losses.
•Need for Comprehensive Risk Assessment: Regularly reassessing the risk of complex financial products is crucial.
•Value of Diversification: Diversifying investments across different asset classes can mitigate risk.
Case Study 2: The Flash Crash of 2010
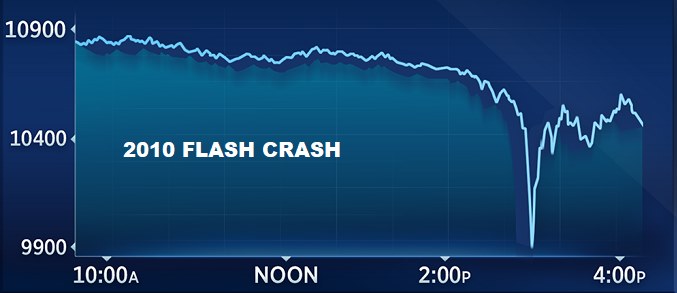
Overview:
On May 6, 2010, U.S. stock markets experienced a rapid and severe decline, followed by a quick recovery. This event is known as the Flash Crash. Within minutes, major stock indices plummeted, causing significant panic and confusion among traders.
What Went Wrong:
- Algorithmic Trading: High-frequency trading algorithms contributed to the rapid price decline.
- Lack of Safeguards: Insufficient safeguards in trading systems allowed for extreme volatility.
- Market Liquidity: A sudden withdrawal of liquidity exacerbated the price drop.
Lessons Learned:
- Importance of Algorithm Management: Ensuring that trading algorithms have safeguards can prevent extreme market movements.
- Need for Market Safeguards: Implementing circuit breakers and other measures can help stabilize markets during periods of high volatility.
- Significance of Liquidity Management: Maintaining adequate liquidity is essential to handle unexpected market events.
Case Study 3: Warren Buffett’s Long-Term Success
Overview:
Warren Buffett, known as the “Oracle of Omaha,” is one of the most successful investors of all time. His investment philosophy is centered around value investing and long-term growth.
What Went Right:
- Disciplined Investment Approach: Buffett focuses on companies with strong fundamentals and invests for the long term.
- Risk Management: He emphasizes the importance of not losing capital and employs conservative leverage.
- Diversification: Buffett’s portfolio is diversified across various sectors and industries.
Lessons Learned:
- Value of Long-Term Perspective: Investing with a long-term horizon can yield significant returns.
- Importance of Conservative Leverage: Using leverage cautiously can protect against major losses.
- Benefit of Diversification: A diversified portfolio can mitigate risk and enhance stability.
Case Study 4: The LTCM Collapse

Overview:
Long-Term Capital Management (LTCM) was a highly successful hedge fund that collapsed in 1998. The fund used complex mathematical models to trade and initially achieved high returns.
What Went Wrong:
- Overconfidence in Models: LTCM’s reliance on mathematical models led to underestimating risks.
- High Leverage: The fund used excessive leverage, which amplified losses.
- Lack of Diversification: Concentrated positions in certain trades exposed LTCM to significant risks.
Lessons Learned:
- Importance of Model Validation: Regularly validating and updating trading models is crucial.
- Risks of High Leverage: Using high leverage can lead to substantial losses.
- Need for Diversification: Spreading investments across different trades can reduce risk.
Case Study 5: The COVID-19 Market Crash

Overview:
The COVID-19 pandemic triggered a global market crash in March 2020. Stock markets around the world experienced sharp declines as uncertainty and fear gripped investors.
What Went Wrong:
- Market Panic: Rapid selling due to panic led to significant market declines.
- Economic Shutdowns: Lockdowns and economic shutdowns affected various industries, leading to widespread losses.
- Liquidity Crunch: A sudden need for liquidity caused sell-offs in various asset classes.
Lessons Learned
- Importance of Staying Calm: Avoiding panic selling can prevent locking in losses.
- Need for Emergency Plans: Having contingency plans for unexpected events is essential.
- Value of Diversification: Diversified portfolios weathered the storm better than concentrated ones.
These case studies highlight the importance of effective risk management in trading. By analyzing what went right and wrong in these real-world examples, traders can gain valuable insights into the strategies and practices that can help them manage risk effectively and achieve long-term success.
Risk management stands as a pivotal element in trading, significantly influencing long-term success. By understanding and implementing the principles and strategies outlined in this guide, you can safeguard your investments, minimize losses, and achieve consistent returns. Effective risk management is not a one-time task but an ongoing process requiring continuous monitoring and adjustment based on market dynamics and personal circumstances.
Key Takeaways:
- Understanding Risk Management: Grasp the fundamental concepts of identifying, assessing, and prioritizing risks in trading.
- Significance of Risk Management: Preserve capital, ensure sustainability, boost confidence, and achieve consistency in returns.
- Fundamental Principles: Follow the steps of risk identification, assessment, prioritization, mitigation, and monitoring.
- Effective Strategies: Implement diversification, position sizing, stop-loss orders, risk-reward ratios, hedging, and leverage management.
- Advanced Techniques: Utilize Value at Risk (VaR), stress testing, and scenario analysis to gain deeper insights into potential risks.
- Psychological Aspects: Maintain emotional discipline, patience, and a commitment to continuous learning.
- Tools and Resources: Leverage trading platforms, risk management software, and educational materials to enhance your strategies.
- Real-World Applications: Learn from case studies that highlight the successes and failures in risk management.
Checklist for Effective Risk Management:
- Identify and assess potential risks.
- Prioritize risks based on impact and likelihood.
- Implement appropriate risk mitigation strategies.
- Regularly monitor and adjust your strategies.
- Use advanced techniques for deeper risk analysis.
- Maintain emotional discipline and avoid impulsive decisions.
- Continuously educate yourself and adapt to market changes.
Ready to elevate your trading game? Join our trading community at Topaz Global to access exclusive insights, personalized guidance, and a network of like-minded traders. Subscribe to our newsletter for regular updates, tips, and strategies to stay ahead in the markets.
For more detailed information on how you can succeed in this market with our Algo, visit Topaz Global.
By integrating these risk management practices into your trading routine, you can enhance your ability to navigate the complexities of the financial markets, protect your investments, and achieve your trading goals.
Thank you for exploring this comprehensive guide to risk management in trading. We hope you found it informative and actionable. For further insights and personalized guidance, join our trading community at Topaz Global. Together, let’s achieve consistent success in the markets.




